[email protected]
- English English Spanish German French Turkish


How to Structure a Thesis: A Complete Guide
Writing a thesis can be an overwhelming task for many college and graduate students. Managing all the elements associated with a thesis while ensuring that the quality is not compromised can be challenging. However, what is even more strenuous is deciding on a thesis's layout. "How to structure a thesis" is a question that several final-year students struggle to answer. And understandably so, as all colleges and universities have their guidelines for drafting a thesis. However, there is an immutable structure that's common for every thesis. In this brief guide, we will take a look at this structure and analyze each of its components.
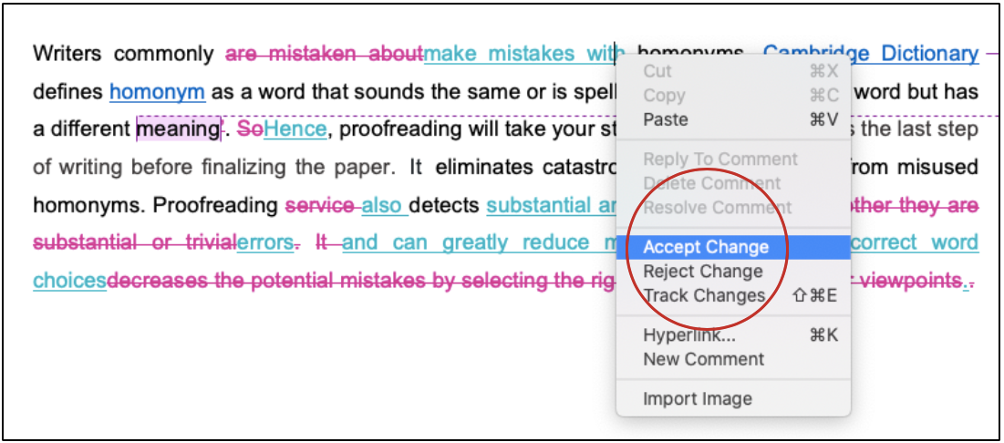
This guide discusses how to structure a thesis effectively. To give you an opportunity to practice proofreading, we have left a few spelling, punctuation, or grammatical errors in the text. See if you can spot them! If you spot the errors correctly, you will be entitled to a 10% discount.
A thesis or dissertation is a long academic document that a master's or doctoral candidate writes to obtain a relevant academic degree. Hence, writing a quality thesis is crucial for college and university students. A good thesis demonstrates a student's academic prowess in their field of study as well as helps hone their analytical and research skills. Writing a thesis can be an overwhelming task for many college and graduate students. Managing all the elements associated with a thesis while ensuring that the quality is not compromised can be challenging. However, what is even more strenuous is deciding on a thesis's layout.
"How to structure a thesis" is a question that several final-year students struggle to answer. And understandably so, as all colleges and universities have their guidelines for drafting a thesis. However, there is an immutable structure that's common for every thesis. In this brief guide, we will take a look at this structure and analyze each of its components. If you are also struggling to initiate the writing process for your thesis, follow this guide and get over your writer’s block.
How to Structure a Thesis: Examining the Constituents of a Thesis Structure
Here we have a list of all major sections that a thesis structure generally comprises. The entire thesis structure is segregated into 3 sections, with each section comprising its relevant subsections to facilitate greater legibility.
Front/Preliminary Matter of a Thesis Structure
1. abstract.
An abstract is a concise summary of an entire thesis and consists of the condensation of your entire thesis. A good abstract is precise, concise (usually not more than 250 words) and emphasizes the importance of the document. When writing an abstract, make sure you explicitly mention the crux of your thesis. Also, avoid reiterating what you have mentioned in the title of your document.
Body of a Thesis Structure
2. introduction/preface.
The introduction chapter of your thesis outlines its core arguments, hypotheses, and results. It is longer than the abstract and contains adequate background information on your topic of interest. Furthermore, it establishes the relevance of your thesis by highlighting its contribution to the knowledge base of its topic. Writing a gripping introduction helps the readers understand the context of your thesis. According to USNSW Sydney, the introduction of a thesis should have the following stages:
State the general topic and give some background
Provide a review of the literature related to the thesis subject
Define the terms and scope of the thesis topic
Outline the existing situation
Evaluate the current situation and identify the gap in the literature
Identify the importance of the proposed research
State the main research questions
State the purpose of the study and/or research objectives
State the study hypotheses
Outline the order of information in the thesis
Outline the methodology.
3. Literature review
The literature review chapter sets the premise of your thesis. It examines and evaluates the research works that’s been conducted so far on your thesis topic and passively highlights the contributions of your thesis.
A literature review is a survey of academic sources on a specific subject, providing an overview of current knowledge, allowing you to discuss relevant theories, methods, and gaps in the existing research. Writing a literature review contains finding relevant publications, critically analyzing the sources, and explaining your findings in the literature. A well-written literature review doesn’t only summarize sources, it also aims to analyze, synthesize, and critically evaluate to give a clear picture of the state of knowledge on the topic.
To write an impeccable literature review, consult a plethora of sources and mention the canon related to your thesis topic. Also, put forward your review in a logical, chronological, and structured manner to better outline the knowledge gaps in your field of study and how your thesis will fill them.

The following simple and straightforward tips can act as the exhaustive rubric and offer meaningful insight to prospective authors on how to formulate a flawless literature review:
Step 1. Probe similar works for a well-structured literature review
Step 2. Analyze, not just synthesize: Authors should provide a detailed critique of the subject
Step 3. Organize your literature review systematically
Step 4. Establish the purview: Authors should specify the scope of the literature review
Step 5. Abstain from plagiarism
Step 6 . Be mindful of the language
4. Methodology
As the name suggests, the methodology section of a thesis consists of all methods and procedures you have used in your thesis. A well-written methodology accentuates the plausibility of your research methods. In addition, it enables your readers to understand why you chose specific methods and how they are justified for your research.
To garner more credibility, you can include the pitfalls and difficulties associated with your choice of research methods. The methodology section is an unavoidable part of a thesis or a research paper. Considering errors in the methodology section enervates the entire thesis.
Follow the steps below to write a perfect methodology for a thesis:
a. Give an outline of the research design
b. Don’t forget to define the philosophy behind the research
c. Mention the research approach
d. Introduce the research methods
e. Note the following points to highlight in the methodology. No matter what methodology you have chosen, you have to focus on the following points:
Explain sampling strategy.
Clearly state the procedure of the research paper.
Mention how you collect the data. (Data collection)
Explain how data are analyzed for your research. (Data analysis). Suppose you have written in qualitative strategy like thematic analysis, mention the researcher you have followed.
Mention the validity of the data and result.
Discuss all ethical aspects of your research paper.
f. Avail professional proofreading and editing services
g. Most important tips to compose an impactful methodology for a dissertation
Don’t drift from your objective and the purpose of your dissertation.
Explore scholarly research papers and their methodology sections to have a better idea.
Plan a proper writing structure.
Understand your audience and target group.
Don’t make mistakes in citing relevant sources. You may use APA and MLA citation
Refer to all the hurdles you have experienced while writing your dissertation.
Make sure to rectify grammatical and punctuation errors.
Ensure that the section is readable and doesn’t consist of long and complex sentences. Long sentences can hamper the tone of the methodology.
This section comprises the outcomes of your research work. It includes all the observations you made and the answers to all your hypotheses in the thesis. When writing the “results” chapter, include only factual data and format it to be distinguishable. Use tables, graphs, subheadings, and generic comments for the results. The aim is to enable your readers to discern the result of your research.
6. Discussion
The discussion chapter of your thesis should begin with a brief summarization of the outcome of your research work. It should explain how your results address your hypotheses and highlight any repetitions in your observations. You can also add comments on how you want the readers to interpret your results and about your agreements and disagreements with the available research work in your field.
Writing a flawless thesis requires much more than only subject matter expertise. It requires expertise, experience, and in-depth thinking, along with sharp intelligence. Though most students add a discussion chapter in their thesis or dissertation, many of them end up messing up the essay or missing out on the central issues.
A discussion chapter in a thesis is a place where you have the chance to delving into the analysis, importance, and relevance of your research. This section focuses on explaining and analyzing what you have researched, presenting how it is associated with the existing literature. It is also a place for argument supporting your entire discussion.
We often find that people seek thesis writing help from experienced editing and proofreading services to prepare a flawless discussion chapter. However, the following helpful tips can help you design a perfect master's or Ph.D.. thesis with an excellent discussion chapter:
Understand the objective of your thesis
Determine a clear structure
Usage of grammar and tense
Refer to hypotheses and literature review
Evaluate your results and compare them with existing studies
Understand the limitation of your research
Don’t be afraid to be unique
Don’t forget to avail a professional thesis editing and proofreading service
Click here to review the details of the aforementioned tips.
The following 5 questions might be helpful to write a sound discussion section:
How well do you understand the objective of your study?
What message is conveyed by your results?
How do your findings compare to findings in literature?
Why should your findings matter?
In what light should your findings be viewed?
7. Conclusion
The final section of your document consists of a precise answer to your hypothesis. In addition, the “conclusion” chapter of your thesis should stress the achievement of the aims of your thesis. You should also include certain limitations of your research to convey the fact that there is still scope for further research in your field.
The end matter of a thesis structure
The components of this section include an acknowledgment, a bibliography, and (occasionally) an appendix.
Parting words
The first step to writing a thesis is to chalk out its layout. Doing so not only helps you deal with the writing process one step at a time but also enables you to better attend to each component of a thesis structure.
Also, before you follow this thesis structure, make sure to check with your university for “how to structure a thesis” guidelines. If the guidelines offered by your institution deviate slightly from what’s mentioned in this guide, then make sure to prioritize the former.
If you need us to make your thesis shine, contact us unhesitatingly!
Best Edit & Proof expert editors and proofreaders focus on offering papers with proper tone, content, and style of academic writing, and also provide an upscale editing and proofreading service for you. If you consider our pieces of advice, you will witness a notable increase in the chance for your research manuscript to be accepted by the publishers. We work together as an academic writing style guide by bestowing subject-area editing and proofreading around several categorized writing styles. With the group of our expert editors, you will always find us all set to help you identify the tone and style that your manuscript needs to get a nod from the publishers.
English formatting service for theses and dissertations
You can also avail of our assistance if you are looking for editors who can format your manuscript, or just check on the particular styles for the formatting task as per the guidelines provided to you, e.g., APA, MLA, or Chicago/Turabian styles. Best Edit & Proof editors and proofreaders provide all sorts of academic writing help, including editing and proofreading services, using our user-friendly website, and a streamlined ordering process.
Get a free quote for editing and proofreading now!
Visit our order page if you want our subject-area editors or language experts to work on your manuscript to improve its tone and style and give it a perfect academic tone and style through proper editing and proofreading. The process of submitting a paper is very easy and quick. Click here to find out how it works.
Our pricing is based on the type of service you avail of here, be it editing or proofreading. We charge on the basis of the word count of your manuscript that you submit for editing and proofreading and the turnaround time it takes to get it done. If you want to get an instant price quote for your project, copy and paste your document or enter your word count into our pricing calculator.

24/7 customer support | Live support
Contact us to get support with academic editing and proofreading. We have a 24/7 active live chat mode to offer you direct support along with qualified editors to refine and furbish your manuscript.

Stay tuned for updated information about editing and proofreading services!
Follow us on Twitter, LinkedIn, Facebook, Instagram, and Medium .
For more posts, click here.
- Editing & Proofreading
- Citation Styles
- Grammar Rules
- Academic Writing
- Proofreading
- Microsoft Tools
- Academic Publishing
- Dissertation & Thesis
- Researching
- Job & Research Application
Similar Posts
How to Determine Variability in a Dataset
How to Determine Central Tendency
How to Specify Study Variables in Research Papers?
Population vs Sample | Sampling Methods for a Dissertation
7 Issues to Avoid That may Dent the Quality of Thesis Writing
How to Ensure the Quality of Academic Writing in a Thesis and Dissertation?
How to Define Population and Sample in a Dissertation?
Recent Posts
ANOVA vs MANOVA: Which Method to Use in Dissertations?
They Also Read

Although the rules of English capitalization seem simple at first glance, it might still be complicated in academic writing. You probably know you should capitalize proper nouns and the first word of every sentence. However, in some cases, capitalization is required for the first word in a quotation and the first word after a colon. In this article, you will find 15 basic capitalization rules for English grammer.

A good part of any research depends on the right questions asked. If you are asking wrong questions, your entire research may go off track. Therefore, understanding what questions you need to ask is essential for your research. If you are on the way to your research but don’t know how to start framing the right research questions, we have just the right information for you. This article discusses the process of formulating research questions.

Academic writing is one of the most systematic writing formats to exist. This type of writing requires you to have precise knowledge about writing formats, style guides and still has additional rules to follow, depending on your type of work. Though it is not something otherworldly and is very much attainable through practice, it can still be a chaotic mess for beginners. A good way to improve yourself is to familiarize yourself with the language rules. In this article, we will take a look at the most important language rules that you must know of and exercise eventually.

An abstract, is an important part of an academic work and a synopsis of a longer study such as a dissertation or thesis. Its most critical aspect is precise reporting of the objectives and outcomes of your research. Thus, the readers can learn about your work by perusing your abstract.

The first chapter of your thesis or dissertation includes the introduction. You should provide the reader with a solid start. Next is staging your research with an apparent focus, objective, and direction.

An abstract usually summarizes a lengthier work (including a dissertation, thesis, research paper, or review). The abstract should explicitly state the objectives and results of your research. Thus, readers can learn what your research addresses.
Anthropomorphism can be defined as attributing human characteristics to nonhuman entities, objects, or concepts. It may lead to ambiguity or misleading communication. Therefore, avoiding anthropomorphism in your thesis, dissertation, or article would be best.
While Sandel argues that pursuing perfection through genetic engineering would decrease our sense of humility, he claims that the sense of solidarity we would lose is also important.
This thesis summarizes several points in Sandel’s argument, but it does not make a claim about how we should understand his argument. A reader who read Sandel’s argument would not also need to read an essay based on this descriptive thesis.
Broad thesis (arguable, but difficult to support with evidence)
Michael Sandel’s arguments about genetic engineering do not take into consideration all the relevant issues.
This is an arguable claim because it would be possible to argue against it by saying that Michael Sandel’s arguments do take all of the relevant issues into consideration. But the claim is too broad. Because the thesis does not specify which “issues” it is focused on—or why it matters if they are considered—readers won’t know what the rest of the essay will argue, and the writer won’t know what to focus on. If there is a particular issue that Sandel does not address, then a more specific version of the thesis would include that issue—hand an explanation of why it is important.
Arguable thesis with analytical claim
While Sandel argues persuasively that our instinct to “remake” (54) ourselves into something ever more perfect is a problem, his belief that we can always draw a line between what is medically necessary and what makes us simply “better than well” (51) is less convincing.
This is an arguable analytical claim. To argue for this claim, the essay writer will need to show how evidence from the article itself points to this interpretation. It’s also a reasonable scope for a thesis because it can be supported with evidence available in the text and is neither too broad nor too narrow.
Arguable thesis with normative claim
Given Sandel’s argument against genetic enhancement, we should not allow parents to decide on using Human Growth Hormone for their children.
This thesis tells us what we should do about a particular issue discussed in Sandel’s article, but it does not tell us how we should understand Sandel’s argument.
Questions to ask about your thesis
- Is the thesis truly arguable? Does it speak to a genuine dilemma in the source, or would most readers automatically agree with it?
- Is the thesis too obvious? Again, would most or all readers agree with it without needing to see your argument?
- Is the thesis complex enough to require a whole essay's worth of argument?
- Is the thesis supportable with evidence from the text rather than with generalizations or outside research?
- Would anyone want to read a paper in which this thesis was developed? That is, can you explain what this paper is adding to our understanding of a problem, question, or topic?
- picture_as_pdf Thesis
- Effective Writing Practices Tutorial
- Organization
- Thesis Statement
A thesis statement expresses the central idea of your written assignment. In essays, a thesis statement is usually included in the introduction. In longer pieces of writing, it may appear further along, but still near the beginning part.
A thesis statement is "your answer to the central question or problem you have raised" (Gibaldi, MLA Handbook for Writers of Research Papers , 50). As you develop your essay or research paper, your thesis may change. Revise it to reflect the scope and the central idea of your writing.
Consider the paragraph below (also discussed in this tutorial's Introduction section):
The University of Illinois envisions an increase in its enrollment to more than 70,000 in under a decade by setting up the Global Campus, a new online education program. While an enrollment of 70,000 students might sound impressive, it is only about half of the current enrollment of the University of Phoenix, a pioneer in online education (Foster, The Chronicle of Higher Education ). The Internet, which has been transforming the landscape of traditional pedagogy in the last few years, is argued to be the most significant development in educational technology in our lifetime. In the last decade, the growth of the Internet has caused various educational institutions and businesses to rethink how they deliver knowledge and information to their learners and to adopt new ways of implementing instruction that takes into consideration recent developments in educational technology. However, in their rush to stay on the cutting edge of technology, some educators look only at the positive features the Internet has to offer and often forget to consider its limitations. The Internet can be extremely valuable for education, but online instruction is not appropriate for all classes in all situations; its implementation needs to be based on the instructor's learning objective, the need for technology, and the availability of resources .
From a student research paper on Advantages and Limitations of Web-Based Instruction :
The central idea or the thesis statement of this student paper is expressed in the last sentence of the introduction.
From the previous example we can observe the following:
It is hard to argue the positive effect of the Internet on teaching and learning, but is all online instruction advantageous?
While, we cannot deny that online instruction is very valuable in education, it may not be suited for all learning situations. The decision to use online instruction should be based the learning objectives, the need for it, and the availability of resources.
Rule To Remember
A thesis statement expresses the central idea of your written assignment.
The rest of the paper then needs to focus on developing the suggested answer to the problem and provide sufficient evidence to support the writer's view.
Writing evolves in stages; sometimes, you may not know what your thesis will be until you start to write. The concept of a working thesis is important here.
A working thesis "should have two parts: a topic part, which states the topic, and a comment part, which makes an important point about the topic" (Lunsford, The Everyday Writer , 36).
When we consider the example from page one again, we can easily point out the topic and the comment components of the working thesis:
Online instruction is not appropriate for all classes in all situations.
Its implementation needs to be based on the instructor's learning objective, the need for it, and the availability of resources.
Another Rule To Remember
Make your thesis statement interesting, specific, and narrow in scope.
A successful thesis has the following characteristics:
- It is interesting to the readers
- It is specific
- It narrows down the scope of the topic to "make it manageable "
(Lunsford, The Everyday Writer , 36)
- Adjective or Adverb
- Commonly Confused Words
- Dangling Modifiers
- Double Negatives
- Inconsistent Verb Tenses
- Misplaced Modifiers
- Parallelism
- Pronoun Agreement
- Relative Clauses
- Split Infinitives
- Subject-verb Agreement
- Use of Numbers
- Capitalization
- Parentheses
- Comma Splice
- Run-on Sentences
- Sentence Fragments
- Reading the Assignment
- Addressing the Audience
- Introduction
- Supporting Paragraphs
- Transitions
- Revision Process
- General Document Format
- Formatting Visuals
- In-text Citations
- In-text Citations in APA Style
- In-text Citations in MLA Style
- List of Sources
- References in APA Style
- MLA Works Cited List
- Bias-free Language
- Formal and Informal Style
- Sentence Structure

- Privacy Policy

Home » Thesis Format – Templates and Samples
Thesis Format – Templates and Samples
- Table of Contents
A thesis format provides a structured framework for presenting research in an organized and academically acceptable manner. It ensures consistency in layout, style, and structure, enabling readers to navigate and understand the document effectively. Whether you are working on an undergraduate thesis, master’s dissertation, or doctoral dissertation, adhering to the correct thesis format is crucial for academic success.
This article explains the essential components of a thesis, provides examples of templates, and includes tips for creating a polished and well-structured document.

Thesis Format
A thesis format refers to the standardized layout and presentation style required for a thesis. It governs elements like font, margins, chapter organization, and referencing style, ensuring that the thesis meets institutional or academic publication standards.
Key Features of a Thesis Format:
- Consistency: Creates a uniform presentation throughout the document.
- Readability: Provides clarity and ease of navigation for readers.
- Compliance: Aligns with institutional guidelines and academic standards.
For example, a university might require 1-inch margins, Times New Roman font size 12, double-spacing, and APA referencing style for all submitted theses.
Components of a Thesis Format
1. title page.
The title page includes the thesis title, author’s name, institution, department, supervisor’s name, and submission date. Some institutions may also require the inclusion of their logo.
Example Title Page:
Title: Exploring the Role of Artificial Intelligence in Education Author: Jane Doe Institution: University of Excellence Program: Master of Science in Computer Science Submission Date: August 2024
2. Abstract
The abstract is a concise summary (150–300 words) that highlights the research objectives, methodology, key findings, and implications. It serves as a snapshot of the entire thesis for readers.
3. Acknowledgments
This optional section allows the author to express gratitude to individuals or organizations that supported their research.
4. Table of Contents
The table of contents lists all chapters, sections, and subsections along with their corresponding page numbers. This section ensures easy navigation for readers.
Example Table of Contents:
- Introduction ……………………………………….. 1
- Literature Review …………………………….. 10
- Methodology ……………………………………. 25
- Results ……………………………………………. 40
- Discussion ……………………………………….. 55
- Conclusion ……………………………………… 70 References ………………………………………………. 80 Appendices ………………………………………………. 90
5. List of Figures and Tables
This section lists all figures and tables in the document, along with their titles and page numbers.
6. Main Body
The main body is the core of the thesis and includes the following sections:
a. Introduction
- Provides background information and context for the research.
- States the research problem, objectives, and questions.
- Outlines the structure of the thesis.
b. Literature Review
- Summarizes and critically evaluates existing research related to the topic.
- Identifies gaps in knowledge and justifies the research.
c. Methodology
- Describes the research design, data collection methods, and analytical techniques used.
- Includes ethical considerations and limitations of the study.
d. Results/Findings
- Presents data in an organized manner using tables, charts, and graphs.
- Focuses on key patterns, trends, and insights.
e. Discussion
- Interprets the findings in relation to the research objectives and existing literature.
- Highlights implications, limitations, and suggestions for future research.
f. Conclusion
- Summarizes the key findings and their significance.
- Reiterates how the research contributes to the field.
7. References/Bibliography
Lists all sources cited in the thesis in the required referencing style (e.g., APA, MLA, Chicago). This section ensures proper attribution and academic integrity.
8. Appendices
Includes supplementary materials such as raw data, questionnaires, interview transcripts, or additional figures.
Thesis Outline
- Thesis Title
- Author’s Name
- Institution Name
- Department/Faculty
- Supervisor’s Name
- Submission Date
A brief summary (150–300 words) covering the research problem, objectives, methods, key findings, and significance.

3. Acknowledgments (Optional)
Expressions of gratitude to individuals or organizations that supported your research.
Lists all sections, chapters, and sub-sections with their corresponding page numbers.
5. List of Figures and Tables (If applicable)
Includes titles and page numbers for all figures and tables used in the thesis.
Chapter 1: Introduction
1.1 Background of the Study 1.2 Research Problem 1.3 Research Objectives 1.4 Research Questions 1.5 Scope of the Study 1.6 Significance of the Study 1.7 Organization of the Thesis
Chapter 2: Literature Review
2.1 Theoretical Framework 2.2 Review of Related Studies 2.3 Identification of Research Gaps
Chapter 3: Methodology
3.1 Research Design 3.2 Sampling Techniques 3.3 Data Collection Methods 3.4 Analytical Tools and Techniques 3.5 Ethical Considerations
Chapter 4: Results/Findings
4.1 Presentation of Data (Tables, Graphs, Charts) 4.2 Analysis and Interpretation of Results
Chapter 5: Discussion
5.1 Summary of Findings 5.2 Comparison with Existing Literature 5.3 Implications of the Findings 5.4 Limitations of the Study
Chapter 6: Conclusion and Recommendations
6.1 Summary of Key Points 6.2 Recommendations for Practice or Policy 6.3 Suggestions for Future Research
7. References
A comprehensive list of all sources cited in the thesis, formatted according to the required referencing style (e.g., APA, MLA, Chicago).
8. Appendices (If applicable)
Includes supplementary materials such as raw data, survey questionnaires, interview transcripts, or additional figures.
Thesis Format Templates
Template 1: standard thesis format.
- Acknowledgments
- List of Figures and Tables
- Introduction
- Literature Review
- Methodology
- Results/Findings
Template 2: APA Style Thesis Format
- Title Page formatted according to APA style.
- Abstract limited to 250 words.
- References following APA citation guidelines.
- Appendices for additional materials.
Tips for Formatting a Thesis
- Follow Institutional Guidelines: Always refer to the specific requirements provided by your institution or department.
- Use Consistent Styles: Ensure uniformity in headings, fonts, and spacing throughout the document.
- Leverage Technology: Use word processing tools like Microsoft Word or LaTeX to create templates and manage references.
- Proofread Carefully: Check for grammatical errors, formatting inconsistencies, and missing references.
- Consult Examples: Review well-structured theses from your institution for guidance.
A well-organized thesis format is essential for presenting research professionally and effectively. By adhering to a structured format and incorporating all necessary components—such as the title page, abstract, methodology, and references—students can ensure their thesis meets academic standards. Using templates and examples as guides, along with careful attention to detail, simplifies the process and ensures a polished final document.
- Creswell, J. W. (2018). Research Design: Qualitative, Quantitative, and Mixed Methods Approaches . Sage Publications.
- Swales, J. M., & Feak, C. B. (2012). Academic Writing for Graduate Students: Essential Tasks and Skills . University of Michigan Press.
- Turabian, K. L. (2018). A Manual for Writers of Research Papers, Theses, and Dissertations . University of Chicago Press.
- American Psychological Association. (2020). Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association (7th ed.).
- The University of Cambridge. (2023). Thesis Formatting Guidelines . [Online resource from institutional repository].
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Dissertation vs Thesis – Key Differences

Delimitations in Research – Types, Examples and...

Significance of the Study – Examples and Writing...

Scope of the Research – Writing Guide and...

Table of Contents – Types, Formats, Examples

APA Table of Contents – Format and Example

- University of Pennsylvania
- School of Arts and Sciences
- Penn Calendar
Search form

Thesis Construction
- On Thesis Statements , by Sam Choi
Welcome to the new OASIS website! We have academic skills, library skills, math and statistics support, and writing resources all together in one new home.

- Walden University
- Faculty Portal
Writing a Paper: Thesis Statements
Basics of thesis statements.
The thesis statement is the brief articulation of your paper's central argument and purpose. You might hear it referred to as simply a "thesis." Every scholarly paper should have a thesis statement, and strong thesis statements are concise, specific, and arguable. Concise means the thesis is short: perhaps one or two sentences for a shorter paper. Specific means the thesis deals with a narrow and focused topic, appropriate to the paper's length. Arguable means that a scholar in your field could disagree (or perhaps already has!).
Strong thesis statements address specific intellectual questions, have clear positions, and use a structure that reflects the overall structure of the paper. Read on to learn more about constructing a strong thesis statement.
Being Specific
This thesis statement has no specific argument:
Needs Improvement: In this essay, I will examine two scholarly articles to find similarities and differences.
This statement is concise, but it is neither specific nor arguable—a reader might wonder, "Which scholarly articles? What is the topic of this paper? What field is the author writing in?" Additionally, the purpose of the paper—to "examine…to find similarities and differences" is not of a scholarly level. Identifying similarities and differences is a good first step, but strong academic argument goes further, analyzing what those similarities and differences might mean or imply.
Better: In this essay, I will argue that Bowler's (2003) autocratic management style, when coupled with Smith's (2007) theory of social cognition, can reduce the expenses associated with employee turnover.
The new revision here is still concise, as well as specific and arguable. We can see that it is specific because the writer is mentioning (a) concrete ideas and (b) exact authors. We can also gather the field (business) and the topic (management and employee turnover). The statement is arguable because the student goes beyond merely comparing; he or she draws conclusions from that comparison ("can reduce the expenses associated with employee turnover").
Making a Unique Argument
This thesis draft repeats the language of the writing prompt without making a unique argument:
Needs Improvement: The purpose of this essay is to monitor, assess, and evaluate an educational program for its strengths and weaknesses. Then, I will provide suggestions for improvement.
You can see here that the student has simply stated the paper's assignment, without articulating specifically how he or she will address it. The student can correct this error simply by phrasing the thesis statement as a specific answer to the assignment prompt.
Better: Through a series of student interviews, I found that Kennedy High School's antibullying program was ineffective. In order to address issues of conflict between students, I argue that Kennedy High School should embrace policies outlined by the California Department of Education (2010).
Words like "ineffective" and "argue" show here that the student has clearly thought through the assignment and analyzed the material; he or she is putting forth a specific and debatable position. The concrete information ("student interviews," "antibullying") further prepares the reader for the body of the paper and demonstrates how the student has addressed the assignment prompt without just restating that language.
Creating a Debate
This thesis statement includes only obvious fact or plot summary instead of argument:
Needs Improvement: Leadership is an important quality in nurse educators.
A good strategy to determine if your thesis statement is too broad (and therefore, not arguable) is to ask yourself, "Would a scholar in my field disagree with this point?" Here, we can see easily that no scholar is likely to argue that leadership is an unimportant quality in nurse educators. The student needs to come up with a more arguable claim, and probably a narrower one; remember that a short paper needs a more focused topic than a dissertation.
Better: Roderick's (2009) theory of participatory leadership is particularly appropriate to nurse educators working within the emergency medicine field, where students benefit most from collegial and kinesthetic learning.
Here, the student has identified a particular type of leadership ("participatory leadership"), narrowing the topic, and has made an arguable claim (this type of leadership is "appropriate" to a specific type of nurse educator). Conceivably, a scholar in the nursing field might disagree with this approach. The student's paper can now proceed, providing specific pieces of evidence to support the arguable central claim.
Choosing the Right Words
This thesis statement uses large or scholarly-sounding words that have no real substance:
Needs Improvement: Scholars should work to seize metacognitive outcomes by harnessing discipline-based networks to empower collaborative infrastructures.
There are many words in this sentence that may be buzzwords in the student's field or key terms taken from other texts, but together they do not communicate a clear, specific meaning. Sometimes students think scholarly writing means constructing complex sentences using special language, but actually it's usually a stronger choice to write clear, simple sentences. When in doubt, remember that your ideas should be complex, not your sentence structure.
Better: Ecologists should work to educate the U.S. public on conservation methods by making use of local and national green organizations to create a widespread communication plan.
Notice in the revision that the field is now clear (ecology), and the language has been made much more field-specific ("conservation methods," "green organizations"), so the reader is able to see concretely the ideas the student is communicating.
Leaving Room for Discussion
This thesis statement is not capable of development or advancement in the paper:
Needs Improvement: There are always alternatives to illegal drug use.
This sample thesis statement makes a claim, but it is not a claim that will sustain extended discussion. This claim is the type of claim that might be appropriate for the conclusion of a paper, but in the beginning of the paper, the student is left with nowhere to go. What further points can be made? If there are "always alternatives" to the problem the student is identifying, then why bother developing a paper around that claim? Ideally, a thesis statement should be complex enough to explore over the length of the entire paper.
Better: The most effective treatment plan for methamphetamine addiction may be a combination of pharmacological and cognitive therapy, as argued by Baker (2008), Smith (2009), and Xavier (2011).
In the revised thesis, you can see the student make a specific, debatable claim that has the potential to generate several pages' worth of discussion. When drafting a thesis statement, think about the questions your thesis statement will generate: What follow-up inquiries might a reader have? In the first example, there are almost no additional questions implied, but the revised example allows for a good deal more exploration.
Thesis Mad Libs
If you are having trouble getting started, try using the models below to generate a rough model of a thesis statement! These models are intended for drafting purposes only and should not appear in your final work.
- In this essay, I argue ____, using ______ to assert _____.
- While scholars have often argued ______, I argue______, because_______.
- Through an analysis of ______, I argue ______, which is important because_______.
Words to Avoid and to Embrace
When drafting your thesis statement, avoid words like explore, investigate, learn, compile, summarize , and explain to describe the main purpose of your paper. These words imply a paper that summarizes or "reports," rather than synthesizing and analyzing.
Instead of the terms above, try words like argue, critique, question , and interrogate . These more analytical words may help you begin strongly, by articulating a specific, critical, scholarly position.
Read Kayla's blog post for tips on taking a stand in a well-crafted thesis statement.
Related Resources
Didn't find what you need? Email us at [email protected] .
- Previous Page: Introductions
- Next Page: Conclusions
- Office of Student Disability Services
Walden Resources
Departments.
- Academic Residencies
- Academic Skills
- Career Planning and Development
- Certification, Licensure and Compliance
- Customer Care Team
- Field Experience
- Military Services
- Student Success Advising
- Writing Skills
Centers and Offices
- Center for Social Change
- Office of Academic Support and Instructional Services
- Office of Degree Acceleration
- Office of Research and Doctoral Services
- Office of Student Affairs
Student Resources
- Doctoral Writing Assessment
- Form & Style Review
- Quick Answers
- ScholarWorks
- SKIL Courses and Workshops
- Walden Bookstore
- Walden Catalog & Student Handbook
- Student Safety/Title IX
- Legal & Consumer Information
- Website Terms and Conditions
- Cookie Policy
- Accessibility
- Accreditation
- State Authorization
- Net Price Calculator
- Cost of Attendance
- Contact Walden
Walden University is a member of Adtalem Global Education, Inc. www.adtalem.com Walden University is certified to operate by SCHEV © 2024 Walden University LLC. All rights reserved.

COMMENTS
What is a thesis? Although the thesis can be found almost anywhere in an essay or other piece of writing, it is usually found at or near the end of the introductory paragraph. The thesis or thesis statement refers to a paper's main argument or central claim. Unlike an ordinary statement (which may merely state a fact or idea), a thesis takes a
A good thesis demonstrates a student's academic prowess in their field of study as well as helps hone their analytical and research skills. Writing a thesis can be an overwhelming task for many college and graduate students. Managing all the elements associated with a thesis while ensuring that the quality is not compromised can be challenging.
A thesis statement is a sentence that sums up the central point of your paper or essay. It usually comes near the end of your introduction. Your thesis will look a bit different depending on the type of essay you're writing. But the thesis statement should always clearly state the main idea you want to get across. Everything else in your ...
Thesis. A thesis is a substantial research document submitted as part of a degree program, typically at the master's or doctoral level. It presents original research findings, explores a specific topic in depth, and contributes to the academic field. Writing a thesis requires thorough planning, a clear structure, and a methodical approach to present arguments and evidence effectively.
Your thesis is the central claim in your essay—your main insight or idea about your source or topic.Your thesis should appear early in an academic essay, followed by a logically constructed argument that supports this central claim. A strong thesis is arguable, which means a thoughtful reader could disagree with it and therefore needs your careful analysis of the evidence to understand how ...
In essays, a thesis statement is usually included in the introduction. In longer pieces of writing, it may appear further along, but still near the beginning part. A thesis statement is "your answer to the central question or problem you have raised" (Gibaldi, MLA Handbook for Writers of Research Papers, 50). As you develop your essay or ...
A thesis format provides a structured framework for presenting research in an organized and academically acceptable manner. It ensures consistency in layout, style, and structure, enabling readers to navigate and understand the document effectively. Whether you are working on an undergraduate thesis, master's dissertation, or doctoral dissertation, adhering to the correct thesis format is ...
Thesis Construction How To Be Original, by Michael Barsanti, which makes more concrete one of the mystified generalities writing teachers like to toss about; related and equally useful is his Writing a Thesis.. Thesis and Introduction Worksheet, Katherine Milligan On Thesis Statements, Hester Blum Erik Simpson's Five Ways of looking at a Thesis, constructed in part by looking at the other ...
The thesis statement is the brief articulation of your paper's central argument and purpose. You might hear it referred to as simply a "thesis." Every scholarly paper should have a thesis statement, and strong thesis statements are concise, specific, and arguable. Concise means the thesis is short: perhaps one or two sentences for a shorter paper.
examine why thesis statements are crucial to a paper. For a Reader Thesis statements act as a roadmap that drive readers from one paragraph to another. Having a thesis statement gives the reader a "notice" on points that will be discussed in the paper. Moreover, having a thesis statement gives the reader a reason to continue reading. Without a